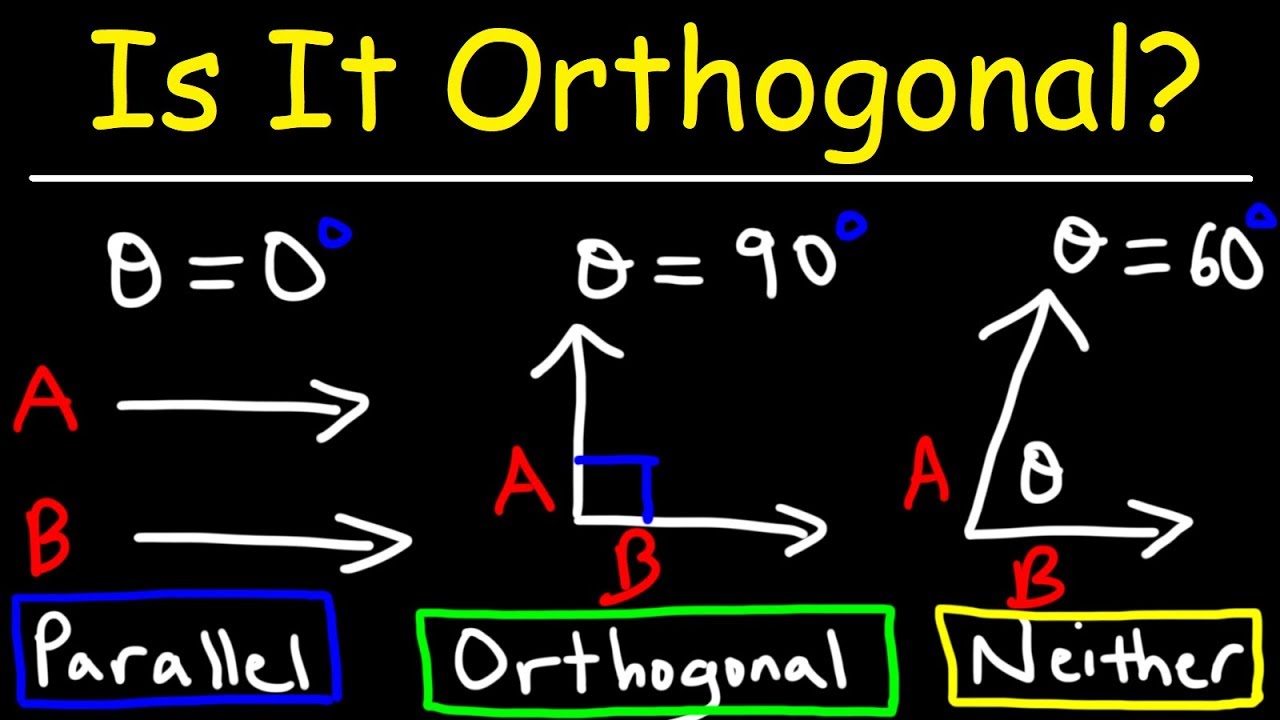
When navigating through the realms of geometry and mathematics, the terms "perpendicular" and "orthogonal" often surface. While they may seem synonymous at a glance, a deeper exploration reveals distinct nuances that set them apart. Understanding these differences is not only vital for students and professionals in math or engineering but also for anyone engaging in discussions involving spatial relationships. The importance of grasping the concepts behind perpendicular vs orthogonal extends beyond mere academic interest; it lays the groundwork for advanced studies in various fields, such as physics, computer science, and architecture.
Both terms deal with the relationships between lines and planes, yet they apply in different contexts. Perpendicular pertains primarily to the intersection of two lines that meet at a right angle (90 degrees), while orthogonal extends this idea to higher dimensions, including vectors and functions. As we delve into the specifics of these terms, we will uncover how they are applied and their implications in real-world scenarios.
In this article, we will dissect the term “perpendicular vs orthogonal,” exploring their definitions, applications, and differences. Whether you are a student trying to ace your geometry test or a professional seeking to refine your understanding of spatial concepts, this comprehensive guide will illuminate the essential characteristics of these two terms.
What Does Perpendicular Mean?
Perpendicular is a term that describes the relationship between two lines or planes that intersect at a right angle (90 degrees). This concept is foundational in geometry and is often used to define various shapes and structures. When two lines are perpendicular, they form a right triangle, which is a critical component of many mathematical principles.
Examples of Perpendicular Lines
Some common examples of perpendicular lines include:
- The edges of a square or rectangle.
- The intersection of the x-axis and y-axis in a Cartesian coordinate system.
- The sides of a right-angled triangle.
What Does Orthogonal Mean?
Orthogonal is a broader term that generally refers to the concept of perpendicularity in higher dimensions. It is commonly used in fields such as linear algebra, where orthogonality describes the relationship between vectors. Two vectors are considered orthogonal if their dot product is zero, implying they are at right angles to each other in a multi-dimensional space.
Applications of Orthogonality
Orthogonality plays a crucial role in various applications, including:
- Signal processing, where orthogonal functions are employed to separate different signals.
- Machine learning, where orthogonal transformations help in data dimensionality reduction.
- Computer graphics, where orthogonal projections are utilized to render 3D images on a 2D screen.
How Are Perpendicular and Orthogonal Related?
Both perpendicular and orthogonal describe similar concepts of right angles, but the primary distinction lies in their contexts of application. While perpendicular is a term mostly used in Euclidean geometry to refer to lines and planes, orthogonal extends this idea to vectors and functions, making it applicable in higher-dimensional spaces.
Real-World Examples of Perpendicular vs Orthogonal
To illustrate the differences further, let's consider a few real-world examples:
- A carpenter creating a right angle corner using a framing square exemplifies perpendicular lines.
- In a 3D modeling program, orthogonal projections are used to view objects from different angles without distortion.
What Are the Key Differences Between Perpendicular vs Orthogonal?
While both terms indicate a relationship involving right angles, the differences can be summarized as follows:
| Feature | Perpendicular | Orthogonal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lines or planes that intersect at 90 degrees | Vectors or functions that are independent, with a dot product of zero |
| Application | Used primarily in geometry | Used in linear algebra and higher dimensions |
| Dimensions | Primarily 2D and 3D | Can be applied in multi-dimensional spaces |
Why Is Understanding Perpendicular vs Orthogonal Important?
Grasping the differences between perpendicular and orthogonal is essential for several reasons. In mathematics and engineering, a clear understanding of these concepts can lead to more effective problem-solving and design. Moreover, the distinction can influence how we approach various fields, from physics to computer science.
Can Perpendicular Lines Be Orthogonal?
Yes, perpendicular lines can be considered orthogonal when discussing them in vector terms. When two lines are perpendicular, they are at a right angle to each other, which means their corresponding vectors are orthogonal. This relationship showcases the interconnectedness of these concepts in different mathematical contexts.
Conclusion: Mastering Perpendicular vs Orthogonal
In summary, while the terms perpendicular and orthogonal both relate to the idea of right angles, they serve distinct purposes in mathematics and geometry. Understanding these differences can enhance one’s comprehension of spatial relationships and their applications in various fields. Whether you are tackling geometry homework or diving into advanced mathematical theories, having a solid grasp of perpendicular vs orthogonal will undoubtedly enrich your learning experience.
Article Recommendations
- Ap Precalculus Unit 3 Review
- Gen Tullos
- Opera Singer Marina Viotti
- Napoleon A Concise Biography
- Drinking Ambien
- Melting Temperature Of Wax
- Large Living Room Cabinet
- Hdfs Copy To Local
- Night Of The Living Deb Script
- How To Turn Off Volte