When it comes to understanding chemical compounds, one of the most intriguing questions lies in the nature of their bonds. Among these compounds, magnesium chloride is often a topic of discussion due to its widespread use in various applications, from de-icing roads to acting as a supplement. A common inquiry is whether magnesium chloride is ionic or covalent. This question not only touches on the fundamental aspects of chemistry but also helps in grasping the properties and behaviors of such compounds. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of magnesium chloride, exploring its structure, bonding nature, and practical implications. Understanding the type of bond in magnesium chloride can lead to deeper insights into its reactivity, solubility, and overall behavior in different environments.
The classification of bonds in compounds can significantly affect their physical and chemical properties. Magnesium chloride, composed of magnesium and chlorine atoms, exhibits unique traits that stem from its bonding nature. By analyzing its ionic and covalent characteristics, we can better appreciate its role in various scientific and industrial applications. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply curious about chemistry, understanding this compound can enhance your knowledge of chemical interactions and materials.
Join us as we explore the fascinating world of magnesium chloride, addressing key questions and uncovering the science behind its bonds. From its molecular structure to its everyday uses, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of whether magnesium chloride is ionic or covalent. Let’s embark on this chemical journey together!
What is Magnesium Chloride?
Magnesium chloride (MgCl₂) is a chemical compound made up of magnesium and chlorine. It is often found in various forms, including anhydrous magnesium chloride, hexahydrate, and other hydrated forms depending on its moisture content. This compound is highly soluble in water and is commonly used in a variety of applications, such as:
- De-icing roads in winter
- As a supplement for magnesium deficiency
- In the production of textiles and paper
- As a coagulant in tofu production
What Type of Bonding Exists in Magnesium Chloride?
To determine whether magnesium chloride is ionic or covalent, we need to examine the nature of the bonds between its constituent atoms. In ionic bonding, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of charged ions. In contrast, covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms.
How Are Ionic Bonds Formed?
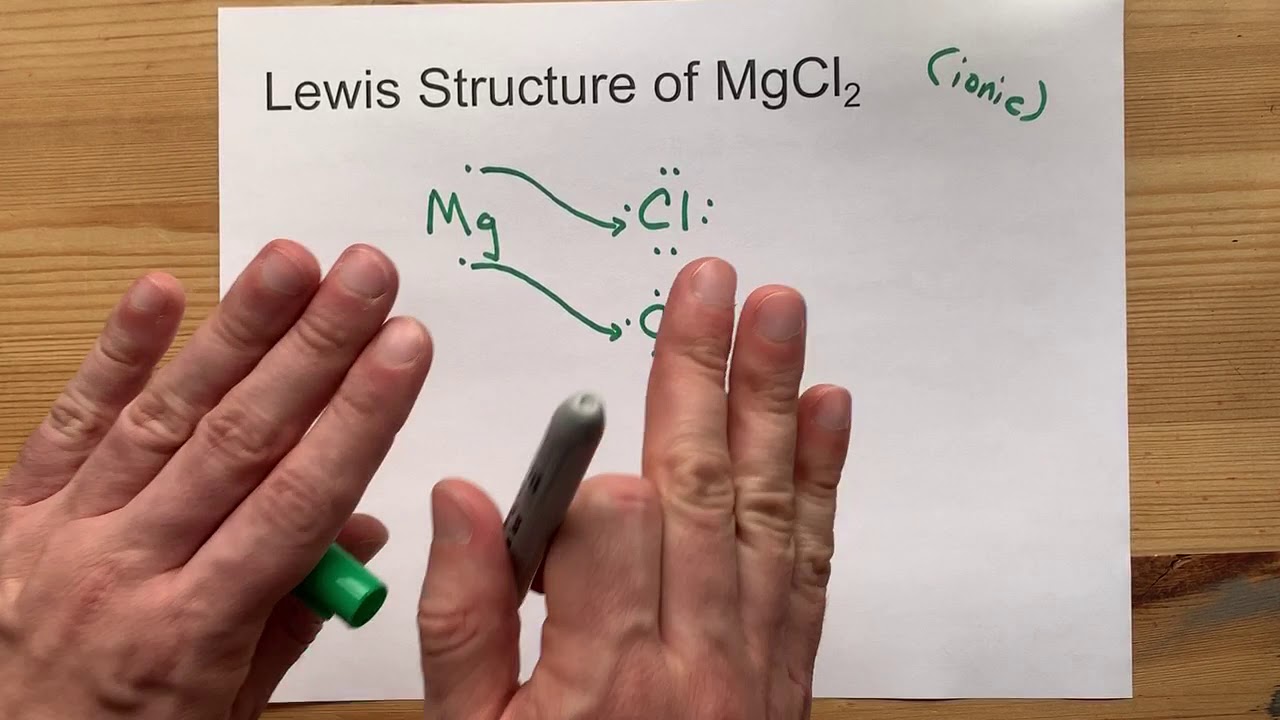
Ionic bonds typically form between metals and nonmetals. In the case of magnesium chloride, magnesium (a metal) loses two electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration, resulting in a positively charged ion (Mg²⁺). On the other hand, chlorine (a nonmetal) gains an electron to form a negatively charged ion (Cl⁻). The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions creates a strong ionic bond, leading to the formation of magnesium chloride.
Is Magnesium Chloride Ionic or Covalent?
Based on the bonding characteristics outlined above, magnesium chloride is primarily classified as an ionic compound. The transfer of electrons from magnesium to chlorine results in the formation of ions, which are held together by strong electrostatic forces. However, it is important to note that in certain conditions, aspects of covalent bonding can also be observed, particularly in the hydrated forms of magnesium chloride.
What Are the Properties of Magnesium Chloride?
The nature of the bonds in magnesium chloride influences its physical and chemical properties. Some key properties include:
- High solubility in water
- High melting and boiling points due to strong ionic bonds
- Electrical conductivity when dissolved in water or molten form
- Hygroscopic nature, allowing it to absorb moisture from the environment
How Does Magnesium Chloride React with Water?
When magnesium chloride is dissolved in water, it dissociates into its constituent ions (Mg²⁺ and Cl⁻). This ionic dissociation is responsible for its high solubility and allows the solution to conduct electricity, demonstrating the properties of ionic compounds. Additionally, the dissolution process can be exothermic, releasing heat.
What Are the Environmental Implications of Magnesium Chloride?
Magnesium chloride's use as a de-icing agent raises questions about its environmental impact. While it is considered less harmful than traditional rock salt, its effects on soil and water quality are still under investigation. Understanding its ionic nature helps in assessing its interactions with the environment and potential long-term consequences.
How Is Magnesium Chloride Used in Daily Life?
Magnesium chloride's versatility allows it to be utilized in various ways in everyday life. Some common applications include:
- As a dietary supplement to promote health
- In agriculture to improve soil quality
- In the food industry as a firming agent in tofu production
- For de-icing roads and sidewalks in winter
Can Magnesium Chloride Be Harmful?
While magnesium chloride has many beneficial uses, it can also pose risks if not handled properly. Exposure to high concentrations may cause irritation to the skin and eyes, and ingestion in large amounts can lead to gastrointestinal distress. It is essential to follow safety guidelines when using magnesium chloride in any application.
Conclusion: Is Magnesium Chloride Ionic or Covalent?
In conclusion, magnesium chloride is primarily categorized as an ionic compound due to the transfer of electrons between magnesium and chlorine atoms. However, certain conditions may exhibit covalent characteristics, particularly in its hydrated forms. Understanding the ionic nature of magnesium chloride provides valuable insights into its properties, applications, and environmental impact. As we continue to explore the world of chemistry, the bonds that hold compounds together remain a fundamental aspect of understanding their behaviors and interactions.
Article Recommendations
- Margot Robbie Weight Gain
- Vogue October 2003
- Solider Costume
- Sarah Lahbati Starstruck
- G3 Case
- Water Dam For House
- Tornado Pro 4 Jacket
- Opera Singer Marina Viotti
- Vegan Restaurants In Sugar Land
- Driving Test Edmond Ok