Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is the fundamental building block of life as we know it. It carries the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms. To truly grasp the significance of DNA, it is essential to explore its structure, which is composed of three critical parts. These components work together in a harmonious fashion to ensure the proper functioning of biological systems. Understanding what are the three parts of DNA molecule will not only deepen your appreciation for the complexity of life but also open doors to the fascinating world of genetics and biotechnology.
The importance of DNA cannot be overstated. From the moment of conception, DNA plays a pivotal role in determining the traits and characteristics of an organism. It is the blueprint that guides the development of every cell, organ, and system within a living being. Moreover, advancements in genetic research have led to groundbreaking discoveries in medicine, agriculture, and forensic science, making it a subject of immense interest across various fields. As we delve deeper into the molecular structure, we will uncover the intricate details of what are the three parts of DNA molecule and their respective functions.
As we navigate through the complexities of DNA, we will also touch upon its implications for future research and technology. By understanding what are the three parts of DNA molecule, we can better appreciate the potential for genetic engineering, gene therapy, and personalized medicine. This exploration will not only illuminate the wonders of life but also pose ethical questions about the manipulation of genetic material. Join us as we embark on this enlightening journey to uncover the secrets of DNA!
What Are the Three Parts of DNA Molecule?
To comprehend the structure of DNA, we must first identify the three essential components that constitute this remarkable molecule:
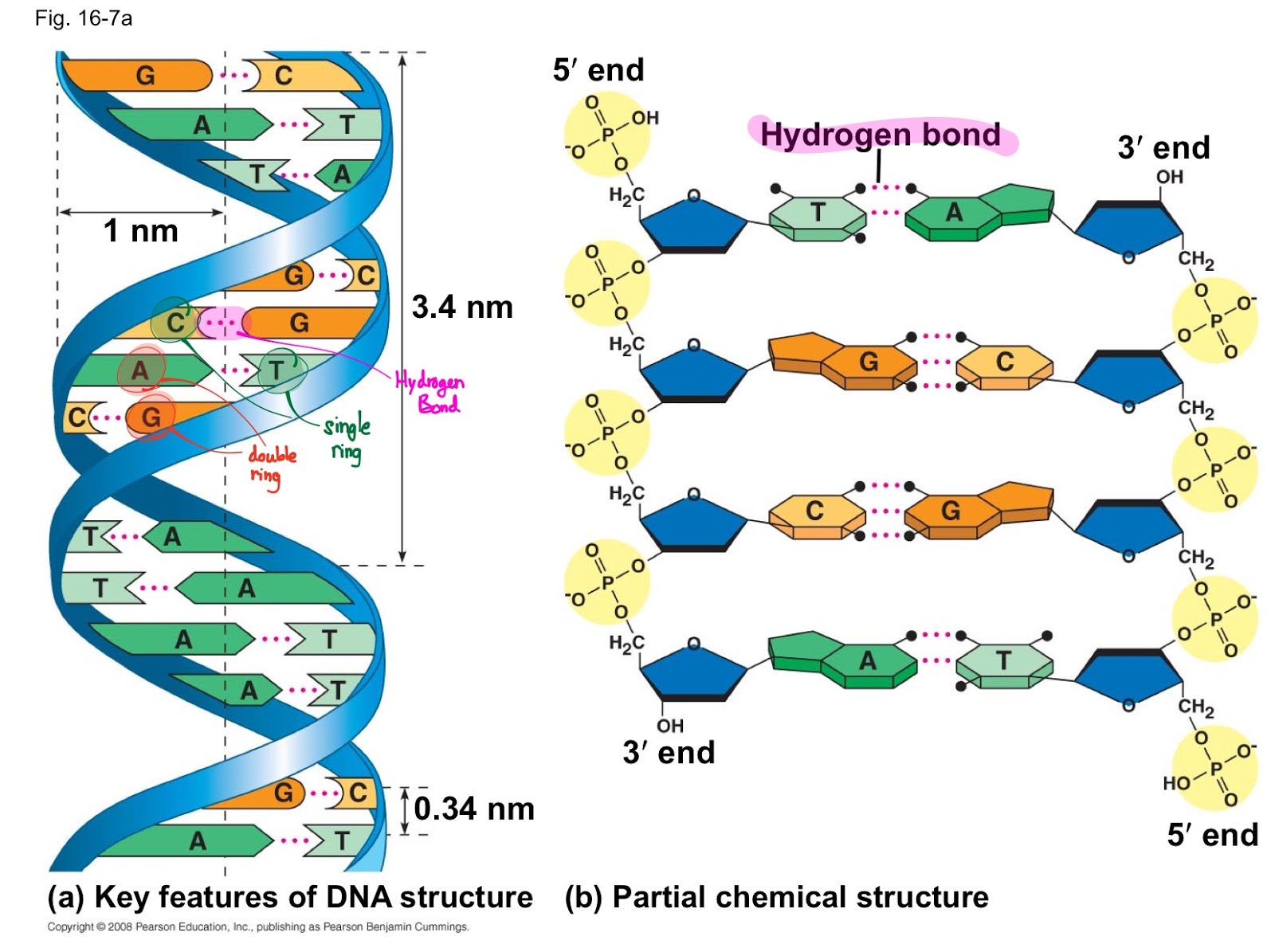
- 1. Sugar (Deoxyribose): The sugar component of DNA is deoxyribose, a five-carbon sugar that forms the backbone of the DNA structure.
- 2. Phosphate Group: The phosphate group is a molecule that consists of phosphorus and oxygen. It links the sugar molecules together, forming the DNA backbone.
- 3. Nitrogenous Bases: These are the building blocks of genetic information and can be categorized into four types: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
How Do These Parts Work Together?
The three parts of DNA work together to create a stable structure known as the double helix. The sugar and phosphate form the outer backbone, while the nitrogenous bases pair in the center. This arrangement is crucial for the storage and transmission of genetic information. The specific sequences of these bases encode the instructions for producing proteins, which are essential for all cellular functions.
What Role Does the Sugar Play in DNA Structure?
The sugar, deoxyribose, serves as a vital component in maintaining the structural integrity of the DNA molecule. It provides a stable framework for the phosphate groups and serves as the attachment point for the nitrogenous bases. The configuration of the sugar molecule also influences the overall shape of DNA, contributing to its double helical structure.
What is the Importance of Phosphate Groups in DNA?
The phosphate groups are crucial for linking the deoxyribose sugars together, forming the backbone of the DNA strand. This connectivity is essential for creating the stable structure that allows DNA to maintain its integrity over generations. Additionally, the negative charge of the phosphate groups contributes to the overall stability of the DNA molecule, allowing it to resist degradation under various environmental conditions.
How Do Nitrogenous Bases Influence Genetic Information?
The nitrogenous bases are the key players in encoding genetic information. The sequence of these bases determines the specific traits and functions of an organism. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine, forming base pairs that are held together by hydrogen bonds. This pairing is essential for DNA replication and protein synthesis, as it allows the genetic code to be accurately copied and translated into functional proteins.
What Are the Implications of Understanding the Three Parts of DNA?
Understanding what are the three parts of DNA molecule has profound implications for various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and forensic science. For instance, in medicine, knowledge of DNA structure has paved the way for gene therapy and personalized medicine, allowing for tailored treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup. In agriculture, genetic engineering has led to the development of crops that are resistant to pests and diseases. Moreover, in forensic science, DNA analysis has revolutionized the way we solve crimes by providing accurate identification of individuals.
What Are the Future Prospects in DNA Research?
The future of DNA research is incredibly promising. As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of genetic material, we can expect advancements in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, which allow for precise modifications to DNA sequences. This could lead to breakthroughs in treating genetic disorders, enhancing agricultural productivity, and even combating climate change through bioengineering. However, with these advancements come ethical considerations regarding genetic manipulation and its potential consequences on society.
Conclusion: The Fascinating World of DNA
In conclusion, understanding what are the three parts of DNA molecule is essential for appreciating the complexity of life and the advancements in genetics. The intricate relationship between sugar, phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases forms the foundation of hereditary information. As we continue to explore the mysteries of DNA, we open new avenues for scientific discovery and innovation that can shape the future of humanity.
Article Recommendations
- Melissa Torme March
- Vegan Restaurants In Sugar Land
- Elasticized Belt
- Gen Tullos
- Ixora Maui Yellow
- Free Attractions In Niagara Falls
- Sherell Ford
- Ap Precalculus Unit 3 Review
- Proofreading Payment
- Glenn Plummer