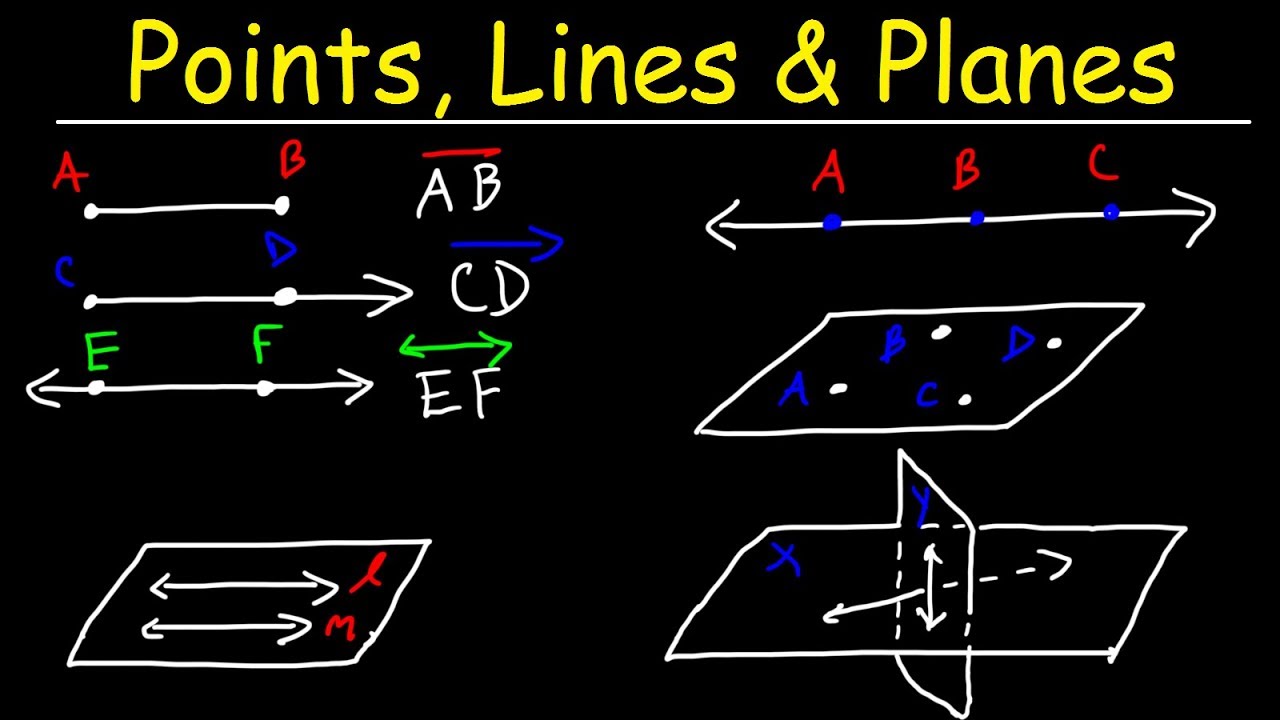
When exploring the fascinating world of geometry, two concepts often come into play: collinear and coplanar points. These terms, while seemingly similar, refer to distinct arrangements in space and have unique implications in various mathematical contexts. Understanding the differences between collinear vs coplanar is essential for students, architects, engineers, and anyone involved in spatial reasoning. Both concepts help us comprehend how points, lines, and planes interact and relate with each other, forming the foundation for more advanced geometric concepts.
Collinear points are those that lie on the same straight line, while coplanar points exist within the same plane. This distinction is critical in geometry, as it helps define the relationships and positioning of shapes and figures. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, characteristics, and applications of collinear and coplanar points, ensuring a thorough understanding of their differences and significance in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Whether you're a student grappling with geometry concepts or a professional applying these principles in design or engineering, grasping the nuances of collinear vs coplanar will enhance your spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills. Let’s embark on this journey to clarify these fundamental geometric terms.
What are Collinear Points?
Collinear points are defined as three or more points that lie on the same straight line. This alignment is essential in various geometric applications, including the study of lines, angles, and shapes. Here are some key features of collinear points:
- All points lie on a single line.
- Collinearity can be established through mathematical equations.
- In a coordinate plane, collinear points can be identified using the slope formula.
How to Determine if Points are Collinear?
To determine if a set of points is collinear, there are several methods, including:
- Using the slope formula: If the slope between any two points is the same for all pairs, they are collinear.
- Using a straightedge: Visually checking if a line can pass through all points.
- Applying the area of a triangle: If the area is zero when calculated using the three points, they are collinear.
Examples of Collinear Points
Consider the points A(1, 2), B(2, 4), and C(3, 6) in a two-dimensional space. If you calculate the slope between A and B and between B and C, you will find them to be equal, confirming that points A, B, and C are collinear.
What are Coplanar Points?
Coplanar points, on the other hand, are defined as points that lie on the same plane. Unlike collinear points, coplanar points do not need to be aligned on a single line. Here are some characteristics of coplanar points:
- They can form various shapes, including triangles and quadrilaterals.
- Coplanarity can be established through geometric proofs.
- In three-dimensional space, coplanar points can be determined by checking if a plane can be created through them.
How to Identify Coplanar Points?
To determine if points are coplanar, consider the following approaches:
- Using the scalar triple product: If the scalar triple product of three vectors is zero, the points are coplanar.
- Visual inspection: If a flat surface can be drawn through the points without interruption, they are coplanar.
- Geometric reasoning: Utilizing the properties of shapes to establish coplanarity.
Examples of Coplanar Points
For instance, consider points P(1, 1, 1), Q(2, 2, 2), R(3, 3, 3), and S(4, 4, 4). These points are coplanar as they can be visualized on a flat plane in three-dimensional space.
Collinear vs Coplanar: What are the Key Differences?
The primary difference between collinear and coplanar points lies in their spatial arrangement. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Collinear Points | Coplanar Points |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Points that lie on the same straight line. | Points that lie in the same plane. |
| Number of Points | At least three points. | At least three points. |
| Mathematical Representation | Slope and linear equations. | Plane equations and vectors. |
| Dimensions | One-dimensional. | Two-dimensional. |
Real-Life Applications of Collinear and Coplanar Points
Understanding collinear vs coplanar is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world applications across various fields:
- Architecture: Ensuring structural integrity by understanding the alignment of beams and supports.
- Engineering: Designing efficient systems that rely on the arrangement of components.
- Computer Graphics: Rendering realistic images by managing points in three-dimensional space.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Analyzing spatial relationships for mapping and urban planning.
Can Points be Both Collinear and Coplanar?
Yes, points can be both collinear and coplanar. In fact, all sets of collinear points are inherently coplanar because any line can be contained within a plane. However, not all coplanar points are collinear; they may form various shapes within that plane.
Conclusion: Why is Understanding Collinear vs Coplanar Important?
Grasping the differences between collinear and coplanar points is crucial for anyone involved in mathematics, engineering, architecture, or any field that requires spatial reasoning. These concepts provide a foundational understanding of how points, lines, and planes interact, allowing for more complex problem-solving and design tasks. By mastering these principles, individuals can enhance their analytical skills and apply them effectively in various professional contexts.
In conclusion, whether you are navigating through geometrical problems in school or applying these concepts in real-world scenarios, a clear understanding of collinear vs coplanar points will serve you well. Embrace the beauty of geometry and its applications in our daily lives!
Article Recommendations
- Brown Tweed Suit Wedding
- Bec And Bridge Bridesmaid
- Macd For Ym
- Horny In Sign Language
- Driving Test Edmond Ok
- G3 Case
- Thyronorm 50mcg
- Bibi Breijman
- Elements Compounds And Mixtures Answer Key
- Cartel Murder Photos