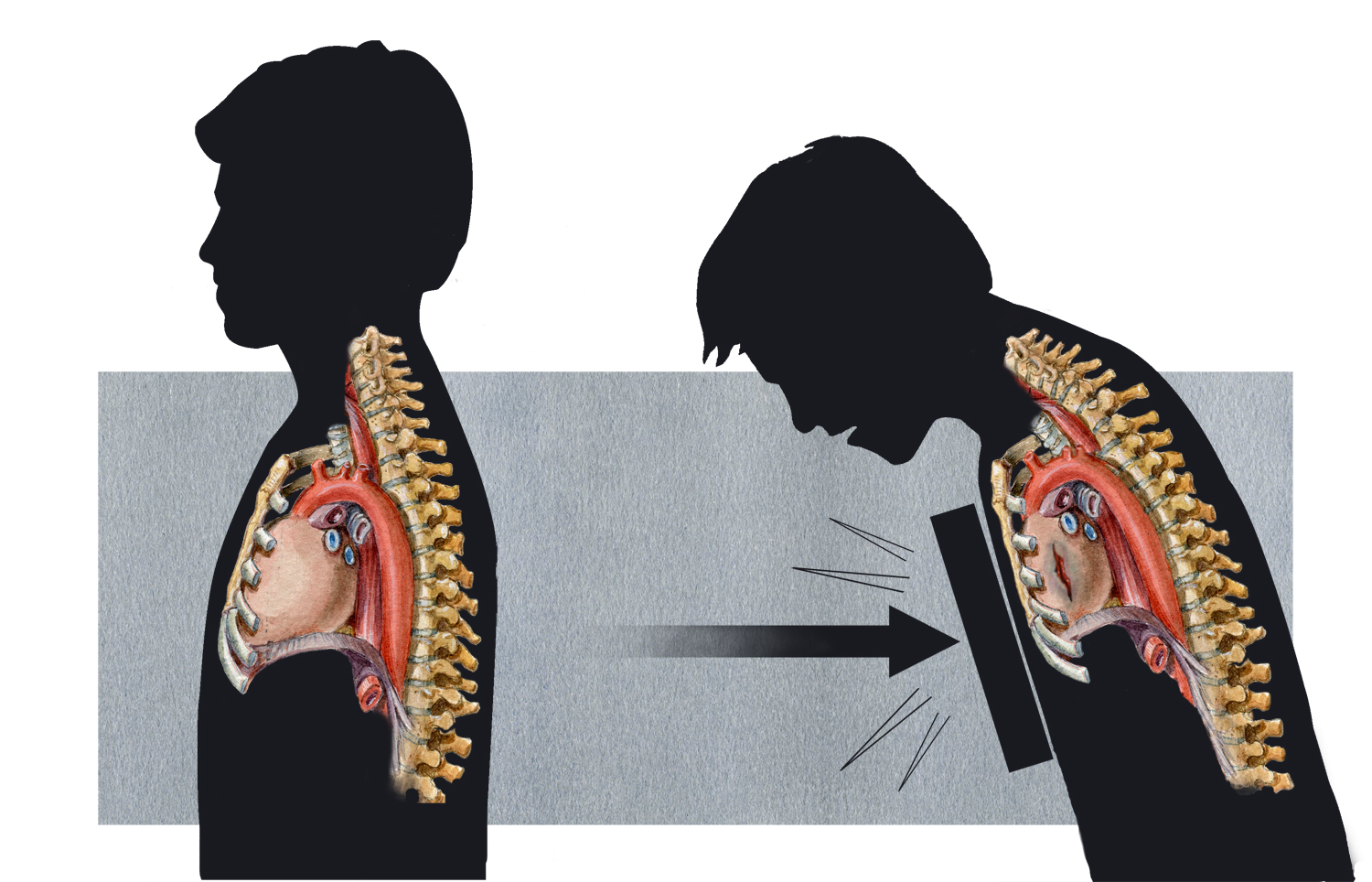
Blunt trauma is a significant medical condition that arises from a forceful impact without penetration of the skin. This type of injury can occur in various situations, including vehicular accidents, falls, and physical assaults. The consequences of blunt trauma can range from minor bruises to severe organ damage, making it essential for individuals to understand its implications and seek prompt medical attention when necessary. In essence, blunt trauma encompasses a wide range of injuries that affect different parts of the body, often leading to complications if not treated properly. The severity of blunt trauma can depend on various factors, including the intensity of the impact, the area of the body affected, and the individual's health condition prior to the injury.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of blunt trauma, examining its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. We will also address common misconceptions about this type of injury and explore the importance of timely medical intervention. By the end of this guide, you will have a clearer understanding of what blunt trauma entails and how to manage it effectively.
Whether you are a medical professional, a caregiver, or simply someone who wants to be informed, understanding blunt trauma is crucial for ensuring proper care and recovery. Let’s explore this significant topic further to enhance our knowledge of blunt trauma and its impact on individuals.
What Causes Blunt Trauma?
Blunt trauma occurs when an object or force strikes the body without breaking the skin. Common causes include:
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Sports injuries
- Falls from heights
- Physical assaults
- Work-related accidents
What Are the Symptoms of Blunt Trauma?
Symptoms of blunt trauma can vary widely based on the severity and location of the injury. Common symptoms may include:
- Bruising or swelling at the impact site
- Pain or tenderness
- Difficulty moving the affected area
- Internal bleeding or organ damage
- Headaches or dizziness (if the head is impacted)
How Is Blunt Trauma Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of blunt trauma typically involves a thorough medical evaluation that may include:
- Medical history assessment
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs
These diagnostic tools help healthcare providers determine the extent of the injuries and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
What Are the Treatment Options for Blunt Trauma?
Treatment for blunt trauma depends on the type and severity of the injury. Options may include:
- Rest and observation for minor injuries
- Medication for pain relief
- Physical therapy for rehabilitation
- Surgery for severe injuries or internal damage
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Blunt Trauma?
Blunt trauma can lead to long-term effects, which may include:
- Chronic pain or discomfort
- Reduced mobility or function
- Psychological effects such as PTSD
- Increased risk of complications like infections
How Can Blunt Trauma Be Prevented?
Prevention strategies for blunt trauma include:
- Wearing seatbelts in vehicles
- Using appropriate protective gear during sports
- Implementing safety measures in workplaces
- Being cautious while climbing or walking on uneven surfaces
What to Do After Experiencing Blunt Trauma?
If you or someone else experiences blunt trauma, it is important to take immediate action:
- Seek medical attention as soon as possible
- Monitor for any changes in symptoms
- Follow all medical advice and treatment plans
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness Regarding Blunt Trauma
Understanding what blunt trauma is and its potential impacts can significantly affect the outcomes for individuals who experience such injuries. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, we can better prepare ourselves and others to respond effectively in emergency situations. Awareness and timely intervention can make a substantial difference in recovery and long-term health.
Article Recommendations
- Water Dam For House
- Morgan Kay Beamer
- Cars With Great Audio Systems
- Chelsea Hobbs
- Freddie Prinze Jr Jessica Biel
- Claudia Gerini
- Driving Test Edmond Ok
- Encroachment Easement
- Sarah Lahbati Starstruck
- Drinking Ambien