The demand curve is a fundamental concept in economics, representing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded by consumers. When we talk about the demand curve, we often refer to its movements and shifts, which can significantly impact market dynamics. Understanding the causes of these shifts is essential for businesses, policymakers, and economists alike, as it provides insights into consumer behavior and market trends. These shifts can signify changes in consumer preferences, income levels, or even external factors such as government policies or global events. In this article, we will explore what are the causes of shift in demand curve, highlighting the various factors that can lead to a change in demand for a particular good or service.
Shifts in the demand curve do not happen in isolation; they are influenced by a multitude of factors, both internal and external to the economy. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will examine specific elements such as price changes, consumer income, preferences, and the effects of substitutes and complements on demand. By understanding these components, stakeholders can better predict market movements and make informed decisions. Ultimately, grasping what are the causes of shift in demand curve is crucial for adapting to ever-evolving market conditions.
Moreover, the interplay between these factors leads to varying degrees of demand changes, which can create opportunities or challenges for businesses. In the following sections, we will answer key questions surrounding this topic, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding the dynamics of demand and its shifts in the marketplace. So let's dive into the intricacies of demand and uncover the causes behind its fluctuations.
What Factors Cause the Demand Curve to Shift?
The demand curve can shift due to a variety of factors. Understanding what are the causes of shift in demand curve is essential for anyone involved in market analysis. Here are some of the primary causes:
- Consumer Preferences: Changes in consumer tastes and preferences can lead to shifts in demand. For example, if a new trend emerges that makes organic foods more popular, the demand for organic produce may increase, shifting the curve to the right.
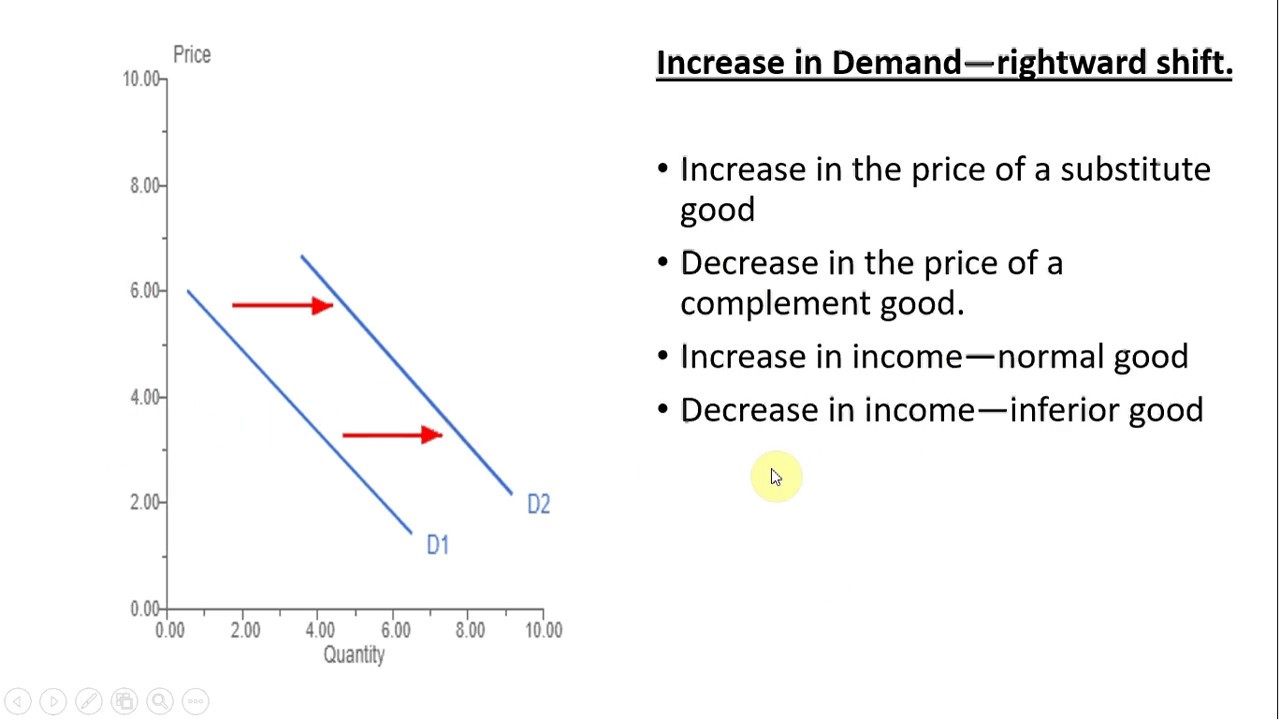
- Income Levels: An increase or decrease in consumer income can significantly affect demand. Typically, as income rises, the demand for normal goods increases, causing a rightward shift in the curve.
- Prices of Related Goods: The demand for a product can be influenced by the prices of substitutes and complements. If the price of a substitute decreases, consumers may opt for the cheaper option, leading to a leftward shift in the demand for the original product.
- Future Expectations: If consumers expect prices to rise in the future, they may purchase more now, increasing current demand and shifting the curve to the right.
- Population Changes: An increase in population can lead to greater demand for goods and services, shifting the demand curve to the right.
- Advertising and Marketing: Effective advertising can enhance consumer awareness and preferences, leading to an increase in demand.
- Seasonal Factors: Certain products experience demand shifts based on seasons, such as winter clothing in the colder months.
- Government Policies: Changes in taxation or regulations can also affect demand. For instance, subsidies on electric vehicles may lead to an increase in demand for those vehicles.
How Do Changes in Consumer Preferences Affect the Demand Curve?
Changes in consumer preferences are one of the most immediate causes of a shift in the demand curve. When consumers develop a preference for a particular product, demand increases, resulting in a rightward shift. Conversely, if preferences shift away from a product, demand decreases, leading to a leftward shift. This can be seen in various industries, from technology to fashion.
What Role Does Income Play in Demand Shifts?
Income plays a critical role in determining demand. As previously mentioned, an increase in income typically leads to a higher demand for normal goods. However, for inferior goods, demand may decrease as income rises. Understanding the relationship between income levels and demand is crucial for businesses aiming to adjust their offerings according to market conditions.
How Do Prices of Related Goods Impact Demand?
The prices of related goods can have a significant effect on the demand for a particular product. For instance, if the price of coffee rises, consumers may switch to tea, leading to a decrease in the demand for coffee. Conversely, if the price of tea decreases, it may attract coffee drinkers, increasing its demand. This interplay highlights the importance of understanding market dynamics when analyzing demand shifts.
What Future Expectations Influence Demand Shifts?
Consumer expectations about future prices can lead to immediate shifts in demand. If consumers anticipate a price increase, they may rush to purchase goods, causing a spike in current demand. Conversely, if they expect prices to fall, they may delay purchases, resulting in a decrease in demand. Businesses need to be aware of these psychological factors when forecasting sales and setting prices.
What Impact Do Population Changes Have on Demand?
Population changes can create significant shifts in demand. An increase in population generally leads to a higher demand for various goods and services, from housing to food. Conversely, a declining population may result in decreased demand and market contraction. Understanding demographic trends is crucial for businesses and policymakers aiming to cater to future market needs.
How Do Advertising and Marketing Affect Demand Shifts?
Effective advertising and marketing strategies can significantly influence consumer preferences and increase demand. By creating awareness and highlighting the benefits of a product, companies can shift the demand curve to the right. This is especially evident in competitive markets where brands vie for consumer attention.
What Role Do Seasonal Factors Play in Demand Shifts?
Seasonal factors can lead to predictable shifts in demand. For example, demand for winter clothing increases during colder months, while demand for ice cream peaks in summer. Businesses must plan for these seasonal fluctuations to manage inventory and maximize sales throughout the year.
How Do Government Policies Affect Demand?
Government policies can have a profound impact on demand. For instance, subsidies for renewable energy can increase demand for electric vehicles, while high taxes on sugary drinks may decrease their demand. Understanding the regulatory environment is essential for businesses to adapt and thrive.
In conclusion, shifts in the demand curve are influenced by various factors, including consumer preferences, income levels, prices of related goods, future expectations, population changes, advertising efforts, seasonal factors, and government policies. By understanding what are the causes of shift in demand curve, stakeholders can make better decisions, anticipate market trends, and develop strategies to meet consumer needs effectively.
Article Recommendations
- Vegan Restaurants In Sugar Land
- How To Use Rabbitfx
- Vogue October 2003
- Lisa Raye Height
- Bibi Breijman
- Claudia Gerini
- Melting Temperature Of Wax
- Morgan Kay Beamer
- Quality Metal Detectors
- Thyronorm 50mcg