Are you experiencing slow internet browsing or facing issues with website access on your Mac? The culprit could be your cached DNS information. In this article, we will explore the essential process of flushing the DNS cache on your Mac using the terminal. Flushing your DNS cache can resolve many connectivity problems and improve your overall browsing experience. Understanding how to execute a DNS flush using the terminal can empower you to take control of your network and enhance your productivity. This guide will break down everything you need to know about performing a DNS flush on your Mac, including step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting tips, and some frequently asked questions.
In today's digital age, a reliable internet connection is crucial for both personal and professional endeavors. However, as we browse the web, our devices store DNS information to speed up future requests. While this caching mechanism is generally beneficial, it can sometimes lead to errors, such as outdated or incorrect IP addresses. When this happens, the solution is often as simple as executing a "mac dns flush terminal" command. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can learn how to effectively flush your DNS cache and restore your connection to the online world.
As we delve deeper into the world of DNS management on your Mac, we will address common questions and concerns regarding the process. Whether you are a tech novice or an experienced user, our comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to confidently perform a DNS flush. Let’s jump in and discover how to troubleshoot your network issues using the mac dns flush terminal.
What is DNS and Why is Flushing it Important?
DNS, or Domain Name System, is a fundamental component of the internet that translates human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into machine-readable IP addresses. This process allows your computer to locate and connect to websites. Over time, your Mac stores these translations in a DNS cache to speed up the browsing process. However, when the cache becomes outdated or corrupt, it can lead to various connectivity issues.
How Does Flushing DNS Work?
Flushing the DNS cache essentially clears out the stored information, prompting your system to fetch the most current data from the DNS server instead. This can resolve issues such as:
- Accessing previously visited websites that have changed IP addresses.
- Fixing problems related to loading certain web pages.
- Resolving conflicts arising from cached DNS entries.
When Should You Consider Flushing Your DNS Cache?
There are several scenarios where flushing your DNS cache may be beneficial:
- After changing your network settings or switching to a new internet provider.
- When experiencing slow internet performance or frequent connection drops.
- When you cannot access specific websites or encounter error messages.
How to Perform a Mac DNS Flush Terminal Command?
Flushing your DNS cache on a Mac is a straightforward process that can be accomplished with a few terminal commands. To begin, follow these steps:
- Open the Terminal: You can find the Terminal application in the Utilities folder within Applications or search for it using Spotlight (Cmd + Space).
- Enter the Flush Command: Depending on your macOS version, the command may vary. Here are the commands for different versions:
- macOS Sierra and later:
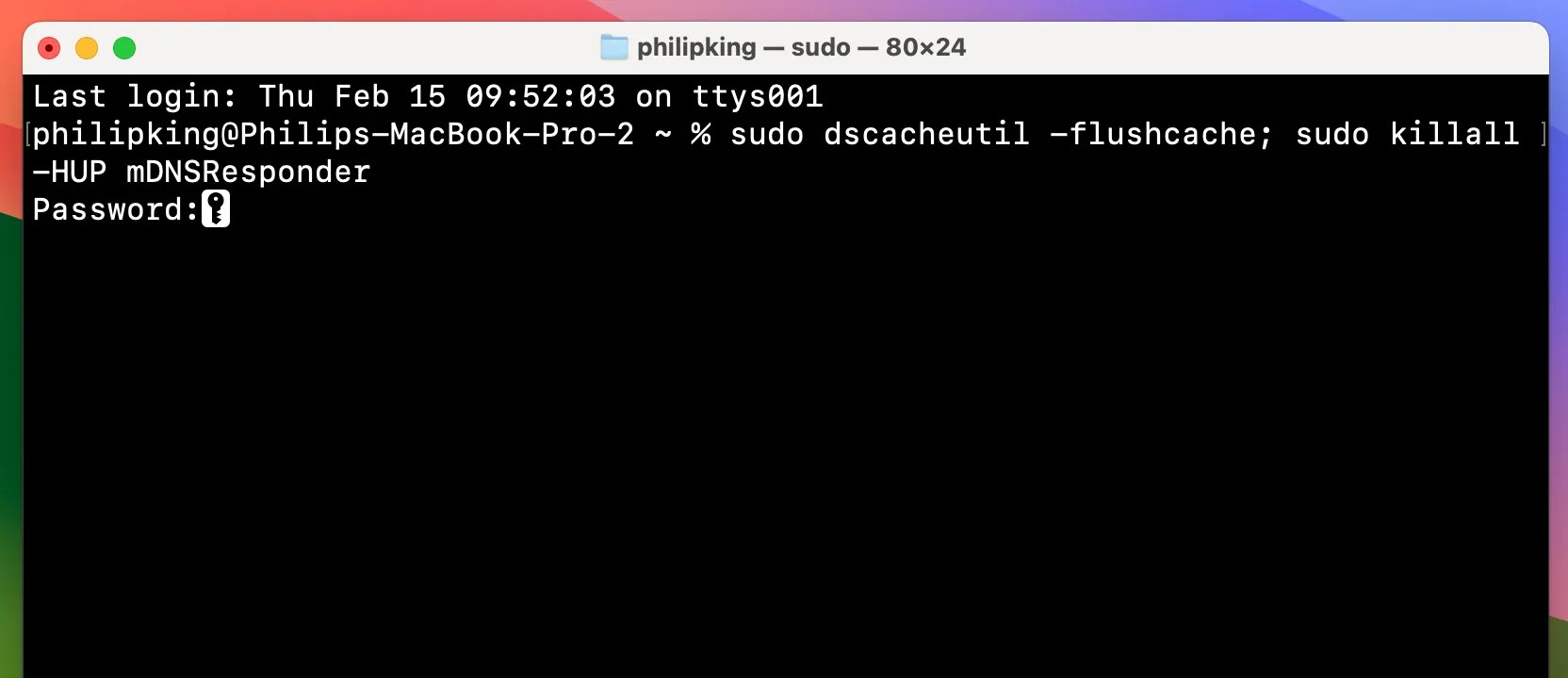
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder - macOS Yosemite:
sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache - macOS Mavericks and earlier:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder - Authenticate: You will be prompted to enter your administrator password. Type it in (note that you won’t see any visual feedback as you type) and press Enter.
- Completion Message: If successful, there won’t be any confirmation message, but you can feel confident that your DNS cache has been flushed.
What to Do if DNS Flushing Doesn’t Solve Your Issues?
If flushing your DNS cache does not resolve your internet issues, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Restart your router or modem.
- Check for software updates on your Mac.
- Try connecting to a different network to determine if the problem is network-specific.
- Contact your internet service provider for further assistance.
Are There Any Risks Involved with Flushing DNS?
The process of flushing your DNS cache is generally safe and poses minimal risks. However, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Temporary disruptions may occur as your system rebuilds its cache.
- After flushing, you may experience slower access to websites initially as new DNS queries are made.
Conclusion: The Importance of Regular DNS Maintenance
In conclusion, understanding how to effectively use the mac dns flush terminal can significantly enhance your online experience. Whether you are dealing with slow connection speeds or website access issues, flushing your DNS cache is a valuable tool in your troubleshooting arsenal. By regularly maintaining your DNS settings, you can ensure that your Mac operates smoothly and efficiently in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Don’t hesitate to revisit this guide whenever you encounter connectivity problems—your Mac's performance may just depend on it!
Article Recommendations
- 3 Way Wiring Diagram
- 80s High Waisted Bikini
- Evergreen Bushes And Shrubs
- Drinking Ambien
- Gta Iv Script Hook
- Proofreading Payment
- Quality Metal Detectors
- Hdfs Copy To Local
- Semi Gloss Polyurethane
- Night Of The Living Deb Script