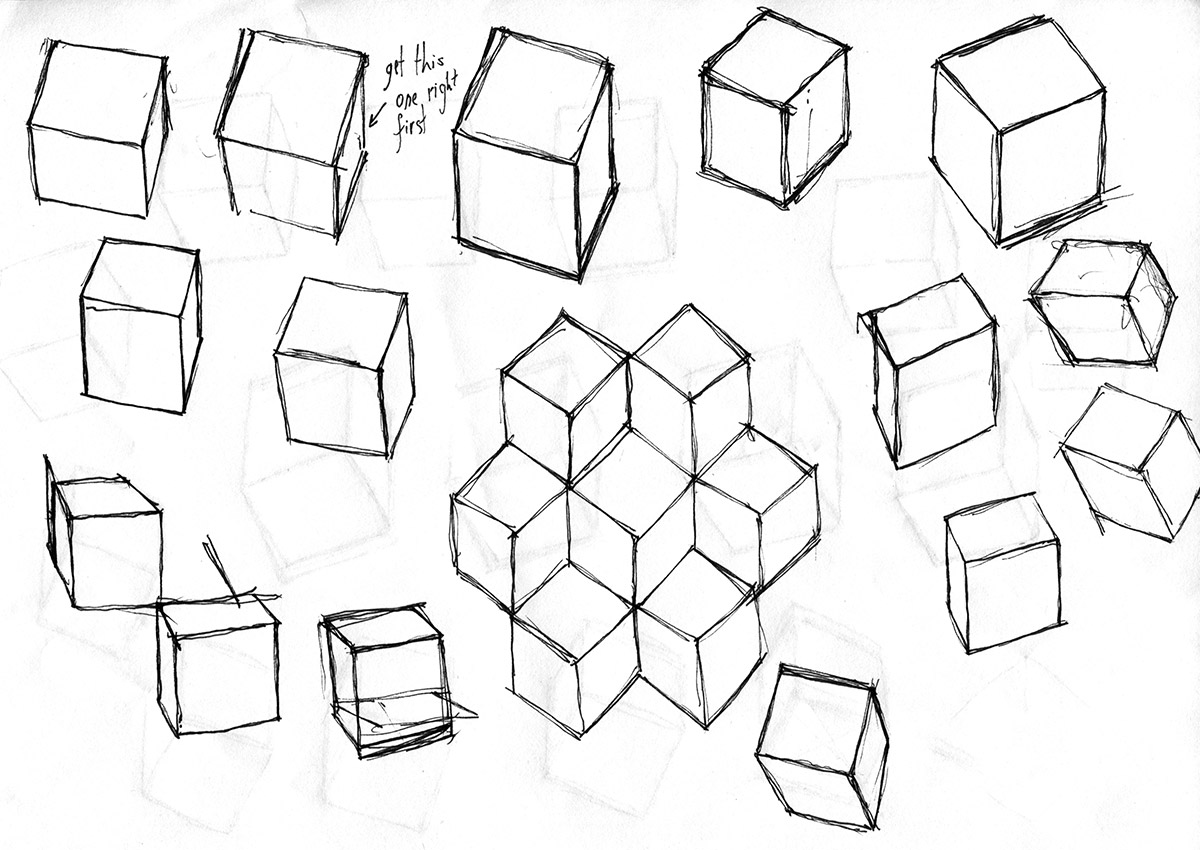
Have you ever wondered how to enhance your drawing skills using simple shapes like cubes? Cubes are fundamental geometric forms that can transform your ability to draw more complex objects. By mastering the art of drawing with cubes, you can gain a clear understanding of perspective, proportion, and dimension, essential skills for any aspiring artist. This guide will take you through a detailed exploration of how cubes can be used to elevate your artistic abilities.
The cube, with its six equal square faces, eight vertices, and twelve edges, is not just a simple shape; it's a building block of artistic design. Whether you're drawing a still life, a character, or an architectural scene, understanding how to break down these subjects into basic cube forms can dramatically improve your drawing accuracy and depth. But how does one begin this journey of using cubes to better their art? Let's dive into the world of drawing with cubes and unlock the secrets to creating dynamic and realistic artworks.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we'll explore various techniques and exercises to help you integrate cubes into your drawing practice. From basic cube construction to complex compositions, each section will provide you with insights and practical steps to enhance your skills. Additionally, we'll delve into the importance of light and shadow, perspective drawing, and how cubes can aid in drawing the human form. By the end of this guide, you'll have a solid foundation to not only draw with cubes but to see the world through the lens of these versatile shapes.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| Understanding the Basics of Cubes |
| Construction of a Cube: Step-by-Step Guide |
| Perspective Drawing with Cubes |
| The Role of Light and Shadow in Cube Drawing |
| Cubes in Composition and Design |
| Drawing Different Objects Using Cubes |
| The Use of Cubes in Architectural Drawings |
| How Cubes Aid in Drawing the Human Form |
| Advanced Techniques: Beyond Basic Cubes |
| Practical Exercises for Mastery |
| Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them |
| Tools and Materials for Drawing with Cubes |
| FAQs about Drawing with Cubes |
| Conclusion: Elevate Your Art with Cubes |
Understanding the Basics of Cubes
Before diving into the complexities of drawing with cubes, it's essential to first understand the basic properties that define a cube. A cube is a three-dimensional shape, also known as a regular hexahedron, characterized by its six square faces, all of which have equal dimensions. This geometric figure also features twelve edges of equal length and eight vertices where three edges meet. Despite its simplicity, the cube serves as a fundamental building block in various artistic disciplines.
One of the key reasons cubes are so integral in art is their ability to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional plane. When artists use cubes in their work, they can better convey depth, proportion, and perspective. Whether you’re drawing a simple object or a complex scene, understanding how to construct and manipulate cubes allows you to break down any subject into manageable parts.
Moreover, cubes can be a versatile tool in learning how to visualize and render light and shadow. Light typically hits a cube in a way that creates distinct planes of light and shadow, helping artists understand how light interacts with three-dimensional forms. By practicing drawing cubes in various lighting conditions, artists can improve their ability to render realistic and dynamic scenes.
Understanding the basics of cubes also involves recognizing their role in mathematics and architecture. In these fields, cubes are valued for their symmetry and stability, often used in the design of buildings, furniture, and even puzzles like the Rubik’s Cube. This knowledge can enrich an artist's appreciation and application of cubes in their work, leading to more thoughtful and intentional designs.
Construction of a Cube: Step-by-Step Guide
Constructing a cube accurately is a crucial skill for any artist interested in utilizing this shape in their drawings. The process of drawing a cube involves understanding basic geometric principles and applying them to create a balanced and proportional representation. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to construct a cube effectively:
Step 1: Draw a Square - Begin by drawing a square, which will serve as the front face of your cube. Ensure that all sides are of equal length for accuracy.
Step 2: Draw a Second Square - Now, draw another square that is slightly offset and behind the first square. This will represent the back face of the cube. It should be parallel and equal in size to the front square.
Step 3: Connect the Corners - Connect the corresponding corners of the two squares with straight lines. These lines will represent the edges of the cube, giving it a three-dimensional appearance.
Step 4: Define the Edges - Make sure that the lines connecting the squares are parallel and of equal length to maintain the cube's proportions.
Step 5: Add Details - Once the basic structure of the cube is in place, you can add details like shading to emphasize its three-dimensional form. Consider the light source's position to create accurate shadows on the cube's surfaces.
By following these steps, artists can create a cube that is visually convincing and serves as a foundation for more complex compositions. Practicing this construction process repeatedly will help solidify the understanding of geometric shapes and their role in art.
Perspective Drawing with Cubes
Perspective drawing is a technique used to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional plane, giving the illusion of depth and space. When drawing with cubes, understanding perspective is crucial for creating artworks that are realistic and visually engaging. There are several types of perspective that artists use, including one-point, two-point, and three-point perspective, each offering a different way to view and draw cubes.
In one-point perspective, all lines converge to a single vanishing point on the horizon. This type of perspective is perfect for drawing objects that are directly facing the viewer, such as a row of cubes aligned along a single axis. By aligning the cube's edges with the vanishing point, artists can create a sense of depth and distance.
Two-point perspective involves two vanishing points on the horizon line, typically used for drawing objects at an angle. This perspective is ideal for drawing cubes that are rotated or viewed from a corner. By using two vanishing points, artists can accurately render the cube's dimensions and spatial relationships, enhancing the realism of their drawings.
Three-point perspective adds a third vanishing point, often used for dramatic compositions where the viewer looks up or down at the cubes. This perspective is perfect for creating dynamic scenes and emphasizing the scale of the cubes. Artists use this technique to convey a more complex sense of space and depth, often seen in architectural drawings and cityscapes.
Mastering perspective drawing with cubes involves practicing these techniques and understanding how to apply them in various artistic contexts. By experimenting with different perspectives, artists can discover new ways to depict cubes and other objects, enriching their creative repertoire.
The Role of Light and Shadow in Cube Drawing
Light and shadow play a critical role in making drawings appear three-dimensional and realistic. When drawing with cubes, understanding how light interacts with their surfaces is essential for creating depth and dimension. The way light falls on a cube can highlight its geometric structure and enhance its visual impact.
The primary aspect of light and shadow is the light source. The position of the light source relative to the cube determines which faces are illuminated and which are in shadow. Artists must decide on a light source before beginning their drawing, as it will influence the entire composition.
The illuminated side of the cube is known as the highlight, where the light hits directly. This area is typically the brightest in the drawing. The shadow side is the part of the cube that is blocked from the light, appearing darker in the drawing. The contrast between these light and shadow areas creates the illusion of depth.
Additionally, artists must consider the cast shadow, which is the shadow the cube projects onto the surface it rests on. This shadow provides context for the cube's placement within the scene, contributing to the overall realism of the drawing.
By practicing how to render light and shadow on cubes, artists can develop a keen understanding of how these elements work together to create three-dimensional forms. This skill can be applied to other shapes and compositions, enhancing the artist's ability to depict realistic and engaging scenes.
Cubes in Composition and Design
Cubes are not only essential for learning basic drawing techniques; they also play a vital role in composition and design. Artists use cubes to organize elements within a composition, creating balance, harmony, and focus. By incorporating cubes into their designs, artists can achieve a more structured and intentional artwork.
In composition, cubes can serve as building blocks to establish the overall structure of the piece. By arranging cubes in various configurations, artists can guide the viewer's eye through the artwork, creating a sense of movement and flow. This technique is often used in abstract and geometric art, where cubes form the foundation of the composition.
Cubes also contribute to the design by providing a framework for other elements. By aligning objects with the edges of cubes, artists can create a cohesive and harmonious design. This approach is commonly seen in architectural drawings, where cubes represent buildings and structures, providing a clear and organized representation of the design.
Additionally, cubes can be used as proportional guides within a composition. By measuring objects against the size of a cube, artists can ensure that their drawings are proportionally accurate and balanced. This technique is particularly useful in still life and figure drawing, where maintaining correct proportions is crucial for realism.
Overall, cubes are a versatile tool in composition and design, offering artists a way to create structured and engaging artworks. By understanding how to use cubes effectively, artists can enhance their creative process and produce more thoughtful and intentional designs.
Drawing Different Objects Using Cubes
Once artists have mastered the basics of drawing cubes, they can use this knowledge to draw a wide range of objects. By breaking down complex forms into basic cube shapes, artists can simplify the drawing process and achieve more accurate representations.
For instance, when drawing still life, artists can use cubes to represent objects like boxes, books, and containers. By starting with a cube as the base shape, artists can easily modify it to match the object's unique features, such as rounded edges or additional details.
In figure drawing, cubes can be used to represent the human body's basic structure. Artists can use cubes to define the torso, limbs, and head, providing a solid foundation for more detailed anatomy. This approach helps artists maintain correct proportions and perspective, leading to more realistic and dynamic figures.
Animals can also be drawn using cubes, breaking down their bodies into manageable shapes. By representing the head, body, and legs as cubes, artists can create a basic framework that can be refined with additional details and features. This technique is particularly useful for capturing the movement and posture of animals.
Overall, using cubes to draw different objects allows artists to simplify complex forms and achieve more accurate and realistic representations. By practicing this technique, artists can expand their drawing repertoire and tackle a wider range of subjects with confidence.
The Use of Cubes in Architectural Drawings
Architectural drawings often rely heavily on geometric shapes, with cubes being one of the most fundamental forms used in this field. Architects and designers use cubes to represent buildings and structures, providing a clear and organized representation of their designs.
In architectural drawings, cubes serve as building blocks that define the basic structure of the design. By arranging cubes in various configurations, architects can create complex and dynamic architectural forms. This approach allows architects to explore different design possibilities and experiment with space and proportion.
Cubes also play a crucial role in perspective drawing in architecture. By using cubes to establish the perspective of a scene, architects can create realistic and accurate representations of their designs. This technique is often used in architectural renderings and visualizations, where conveying the scale and depth of a design is essential.
Additionally, cubes are used as proportional guides in architectural drawings. By measuring the dimensions of a building against the size of a cube, architects can ensure that their designs are proportionally accurate and balanced. This technique is particularly useful when designing complex structures with multiple levels and elements.
Overall, cubes are an essential tool in architectural drawings, offering architects a way to create clear, accurate, and engaging representations of their designs. By understanding how to use cubes effectively, architects can enhance their creative process and produce more thoughtful and intentional designs.
How Cubes Aid in Drawing the Human Form
Drawing the human form can be a challenging task, but using cubes as a foundation can simplify the process and lead to more accurate representations. By breaking down the human body into basic cube shapes, artists can create a solid framework that can be refined with additional details and features.
When drawing the human form, artists can use cubes to represent the torso, limbs, and head. By starting with a cube as the base shape, artists can easily modify it to match the body's unique features, such as curves and angles. This approach helps artists maintain correct proportions and perspective, leading to more realistic and dynamic figures.
Cubes can also be used to establish the pose and posture of the human form. By arranging cubes in various configurations, artists can create a sense of movement and balance within the drawing. This technique is particularly useful for capturing the dynamic poses and gestures of the human body.
Additionally, cubes can serve as proportional guides when drawing the human form. By measuring the dimensions of the body against the size of a cube, artists can ensure that their drawings are proportionally accurate and balanced. This technique is especially useful when drawing complex poses or multiple figures within a scene.
Overall, using cubes to draw the human form allows artists to simplify the process and achieve more accurate and realistic representations. By practicing this technique, artists can expand their drawing repertoire and tackle a wider range of subjects with confidence.
Advanced Techniques: Beyond Basic Cubes
Once artists have mastered the basics of drawing with cubes, they can explore more advanced techniques to enhance their skills and creativity. These techniques involve experimenting with different perspectives, incorporating additional geometric shapes, and using cubes in more complex compositions.
One advanced technique is to experiment with perspective. By using different types of perspective, such as one-point, two-point, and three-point, artists can create dynamic and engaging compositions. This approach allows artists to explore different viewpoints and angles, adding depth and dimension to their drawings.
Another advanced technique is to combine cubes with other geometric shapes. By incorporating shapes like spheres, cylinders, and cones, artists can create more complex and interesting compositions. This technique is particularly useful for creating abstract and geometric art, where different shapes interact and overlap.
Additionally, artists can use cubes in complex compositions, such as architectural renderings and cityscapes. By arranging cubes in various configurations, artists can create a sense of movement and flow within the composition. This technique is often used in architectural drawings, where cubes represent buildings and structures, providing a clear and organized representation of the design.
Overall, advanced techniques in drawing with cubes offer artists a way to enhance their skills and creativity. By experimenting with different perspectives, incorporating additional shapes, and creating complex compositions, artists can expand their creative repertoire and produce more engaging and dynamic artworks.
Practical Exercises for Mastery
Practicing drawing with cubes is essential for mastering this technique and improving overall drawing skills. Here are some practical exercises that artists can use to develop their skills and gain confidence in drawing with cubes:
- Exercise 1: Drawing Cubes from Life - Set up a still life with simple objects like boxes or books, and practice drawing them as cubes. Focus on capturing the proportions, perspective, and light and shadow of each object.
- Exercise 2: Cube Construction - Practice constructing cubes from different angles using one-point, two-point, and three-point perspective. Experiment with different viewpoints and angles to create dynamic compositions.
- Exercise 3: Combining Cubes with Other Shapes - Create compositions by combining cubes with other geometric shapes like spheres, cylinders, and cones. Experiment with different arrangements and overlaps to create interesting and engaging designs.
- Exercise 4: Drawing the Human Form with Cubes - Practice drawing the human form using cubes as a foundation. Focus on capturing the proportions, pose, and posture of the body, and refine the drawing with additional details and features.
- Exercise 5: Architectural Drawings - Practice drawing architectural scenes using cubes to represent buildings and structures. Experiment with different perspectives and compositions to create realistic and engaging renderings.
By practicing these exercises regularly, artists can develop their skills and gain confidence in drawing with cubes. Over time, these exercises will help artists expand their creative repertoire and tackle a wider range of subjects with ease.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When learning to draw with cubes, artists may encounter common mistakes that can hinder their progress and affect the quality of their drawings. Here are some common mistakes and tips on how to avoid them:
- Mistake 1: Inaccurate Proportions - One of the most common mistakes is drawing cubes with inaccurate proportions. To avoid this, artists should use measuring tools and reference guides to ensure that all sides of the cube are equal in length.
- Mistake 2: Poor Perspective - Another common mistake is drawing cubes with poor perspective, leading to a distorted appearance. Artists can avoid this by practicing perspective drawing techniques and using vanishing points to establish the correct angles and proportions.
- Mistake 3: Inconsistent Light and Shadow - Inconsistent light and shadow can make cubes appear flat and unrealistic. To avoid this, artists should establish a clear light source and consistently apply shading to create depth and dimension.
- Mistake 4: Overcomplicating the Drawing - Overcomplicating the drawing with too many details can detract from the overall composition. Artists should focus on capturing the essential elements of the cube and gradually add details as needed.
- Mistake 5: Neglecting Practice - Neglecting regular practice can hinder progress and skill development. Artists should commit to regular practice sessions to improve their drawing skills and gain confidence in using cubes in their work.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, artists can improve their drawing skills and produce more accurate and engaging artworks.
Tools and Materials for Drawing with Cubes
Having the right tools and materials is essential for drawing with cubes effectively. Here are some recommended tools and materials that artists can use to enhance their drawing practice:
- Pencils - A range of pencils from hard to soft (e.g., 2H to 6B) allows artists to create different line weights and shading effects. Mechanical pencils can also be useful for precise lines and details.
- Pens - Fine liners and ink pens can be used for outlining and adding details to drawings. Pens with different nib sizes offer versatility in line work.
- Ruler - A ruler is essential for drawing straight lines and maintaining accurate proportions when constructing cubes.
- Eraser - A good quality eraser is necessary for correcting mistakes and refining drawings. Kneaded erasers are particularly useful for lifting graphite without damaging the paper.
- Drawing Paper - High-quality drawing paper with a smooth surface is ideal for drawing with cubes. Heavier weight paper can handle more layers of shading and detail work.
- Lightbox - A lightbox can be useful for tracing and refining drawings, especially when practicing perspective and proportion techniques.
By investing in quality tools and materials, artists can enhance their drawing practice and achieve better results when drawing with cubes.
FAQs about Drawing with Cubes
Here are some frequently asked questions about drawing with cubes and their answers:
Q1: Why is drawing with cubes important for artists?
A1: Drawing with cubes is important because it helps artists understand perspective, proportion, and dimension, which are essential skills for creating realistic and dynamic artworks.
Q2: How can I improve my cube drawing skills?
A2: To improve your cube drawing skills, practice regularly, focus on accurate proportions, and experiment with different perspectives and compositions.
Q3: Can cubes be used for drawing objects other than buildings and boxes?
A3: Yes, cubes can be used to draw a variety of objects, including figures, animals, and complex scenes. By breaking down forms into basic cube shapes, artists can simplify the drawing process and achieve more accurate representations.
Q4: What are some common mistakes to avoid when drawing with cubes?
A4: Common mistakes include inaccurate proportions, poor perspective, inconsistent light and shadow, overcomplicating the drawing, and neglecting practice. Being aware of these mistakes and taking steps to avoid them can improve your drawing skills.
Q5: What tools and materials are recommended for drawing with cubes?
A5: Recommended tools and materials include a range of pencils, pens, a ruler, erasers, high-quality drawing paper, and a lightbox.
Q6: How can cubes be used in architectural drawings?
A6: In architectural drawings, cubes are used to represent buildings and structures. They serve as building blocks to define the basic structure of the design and can be used to create realistic and engaging renderings through perspective drawing.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Art with Cubes
Drawing with cubes is a powerful technique that can elevate your art by enhancing your understanding of perspective, proportion, and dimension. By mastering the basics of cube construction and exploring advanced techniques, artists can gain confidence and expand their creative repertoire. Whether used in still life, figure drawing, or architectural designs, cubes offer a versatile tool for creating structured and engaging compositions. With regular practice and the right tools, artists can unlock the full potential of drawing with cubes and achieve more accurate and dynamic artworks. So, pick up your pencils and start exploring the endless possibilities that cubes have to offer in your artistic journey.
For more resources and inspiration, consider visiting ArtStation, a platform where artists share their work and connect with a community of creatives.
Article Recommendations
- Emo In Thong
- Glenn Plummer
- Gotlet
- Night Of The Living Deb Script
- Hdfs Copy To Local
- Gta Iv Script Hook
- Margot Robbie Weight Gain
- Robin Sharma Wife
- Thyronorm 50mcg
- Vegan Restaurants In Sugar Land